Business Requirements
Glossary
During the initial analysis phase, we collected the main terms and definitions that will be the basis for the requirements' engineering and the system's design.
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Camera | Device that generates a video stream and sends it to the other parts of the system |
| Sensor | Device capturing sensing data from an environment (e.g. temperature) |
| Device | Either a camera or a sensor |
| Video Stream | Stream of video data produced by a camera |
| Measurement | Data produced by a sensor |
| User | User that can access the system |
| Detection | Recognition of an object in a video stream |
| Intrusion | Detection of an unauthorized object |
| Outlier | Environment value exceeding user defined ranges |
| Anomaly | Either an intrusion or an outlier |
| Security Rule | Rule defined by an user to trigger anomalies in a defined range of time |
| Location | Rooms or buildings where devices are located |
| Notification | An alert sent to the user to inform that an anomaly has been triggered. |
User Creation
There are two main roles: the Admin and the Guardian. When not specified, the role is Guardian.
A registered Admin can create a new user in the system. The user will have access to the system and will be able to consult the devices depending on the location permissions.
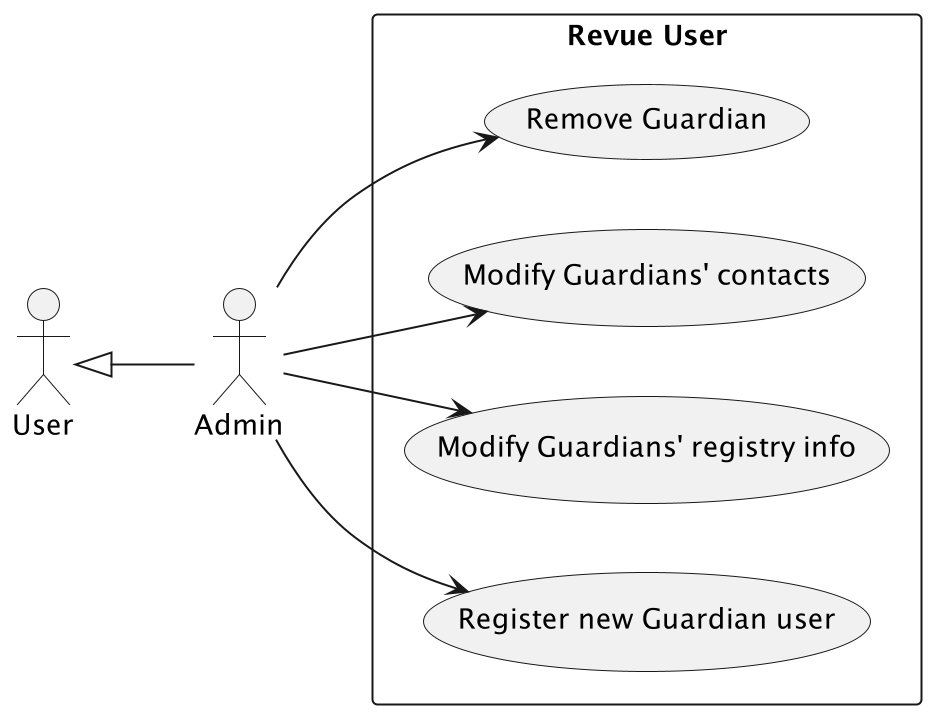
-
Register a new user in the system.
- Actor: Admin
- Precondition: The admin is logged in the system, and the user is not registered yet.
- Post condition: The user is created in the system, can access the system and consult the devices depending on his permissions.
- Flow:
- The admin moves to the "Create User" section.
- The admin fills the user information.
- The admin selects the locations that the user can access.
- The system after precise checks creates the user.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user is created in the system.
- Extensions:
- The user already exists in the system.
- The user information is not filled correctly.
-
Modify user information and permissions.
- Actor: Admin
- Precondition: The admin is logged in the system, and the user is registered.
- Post condition: The user information is updated in the system.
- Flow:
- The admin moves to the "Update User" section.
- The admin selects the user to update.
- The admin updates the user information.
- The admin updates the user permissions.
- The system after precise checks updates the user.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user information is updated in the system.
- Extensions:
- The information is not filled correctly, in this case, the system will not update the user information and will show an error message.
-
Modify user contact information.
- Actor: Admin
- Precondition: The admin is logged in the system, and the user is registered.
- Post condition: The user contact information is updated in the system.
- Flow:
- The admin moves to the "Update User" section.
- The admin selects the user to update.
- The admin updates the user contact information.
- The system updates the user.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user contact information is updated in the system.
-
Delete user.
- Actor: Admin
- Precondition: The admin is logged in the system, and the user is registered.
- Post condition: The user is deleted from the system.
- Flow:
- The admin moves to the "Delete User" section.
- The admin selects the user to delete.
- The system after precise checks deletes the user.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user is deleted from the system.
Location Management
A registered Admin can create a new location in the system. Every device resides in a location. The final user can consult it only if he has access to the location.
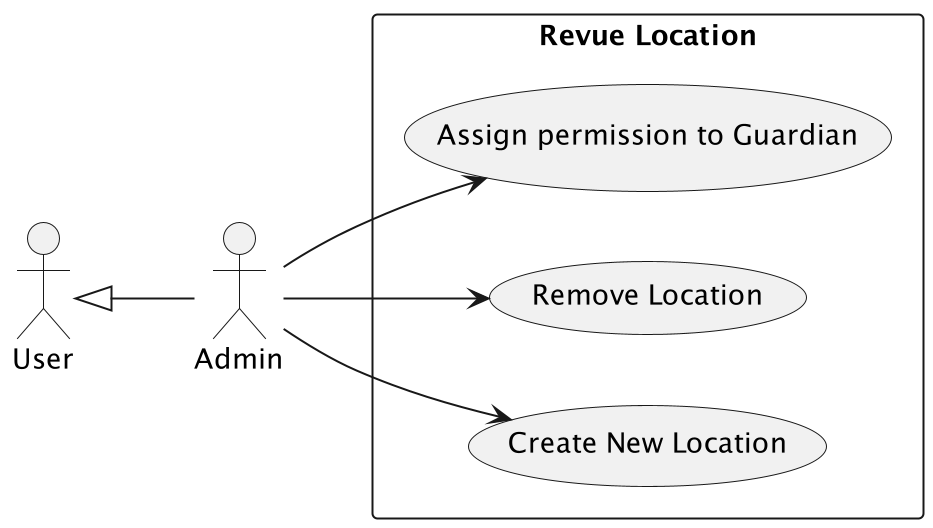
-
Create a new location.
- Actor: Admin
- Precondition: The admin is logged in the system, and the location is not present yet.
- Post condition: The location is created in the system.
- Flow:
- The admin moves to the "Location" section and opens the "Create Location" popup.
- The admin fills the location information.
- The system creates the location.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The location is created in the system.
- The admin can see the location in the location list.
- Extensions:
- The location already exists in the system (error message).
-
Remove location.
- Actor: Admin
- Precondition: The admin is logged in the system, and the location is present.
- Post condition: The location is deleted from the system.
- Flow:
- The admin moves to the "Location" section and selects the location to delete.
- The admin click on the remove icon.
- The system deletes the location.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The location is deleted from the system, and the admin can't see it in the location list.
Device Management
A registered User can federate a device in the system. The user can consult the device information and consult real-time data. Moreover the user can modify the device description.
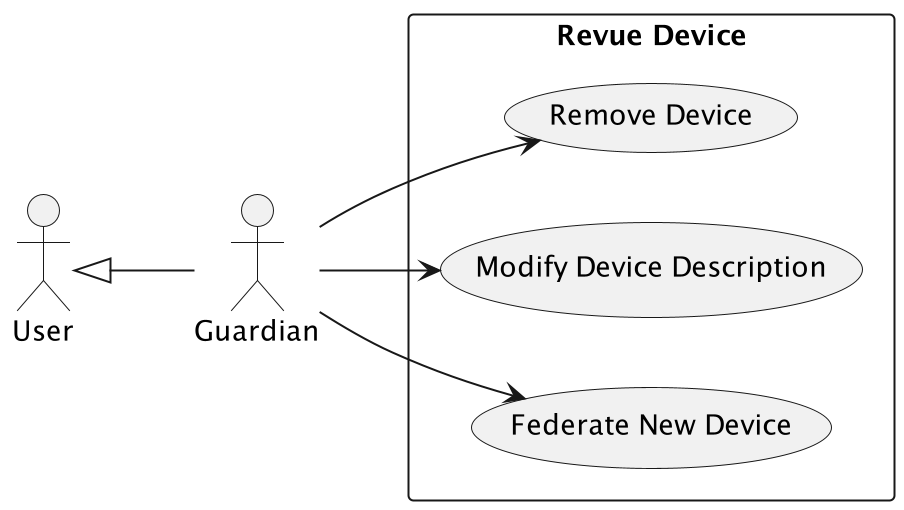
-
Federate a device.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The device has an exposed IP address.
- The device adheres to the system protocol.
- The device exposes some capabilities.
- The device is not federated yet.
- Post condition:
- The device is federated in the system.
- The user can consult the device information.
- The user can consult the real-time data.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Device" section and opens the "Add Device" popup.
- The user fills the device's IP address and port.
- The user clicks the "Retrieve Device Information" button.
- The system retrieves the device information and fills the device information fields.
- The user fills the device description and sees the device's capabilities.
- The user finally selects the "Create" button.
- The system after retrieving device's information federates the device.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The device is federated in the system.
- The user can see the device in the device list.
- The user can consult the device information.
- The user can consult the real-time data according to the device capabilities.
- The user can see precise information about device capabilities.
- Extensions:
- The device is not reachable (error message).
- The device is not compliant with the system protocol (error message).
- The device is already federated in the system (error message).
- The device is reachable and compliant but doesn't expose any capabilities (error message).
-
Modify device description.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The device is federated in the system.
- Post condition:
- The device description is updated in the system.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Device" section and selects the device to update.
- The user clicks on the "Update" button.
- The user updates the device description.
- The system updates the device description.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The device description is updated in the system.
- Extensions:
- The device is not reachable (error message).
-
Remove device.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The device is federated in the system.
- Post condition:
- The device is removed from the system.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Device" section and selects the device to remove.
- The user clicks on the "Remove" button.
- The system removes the device.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The device is removed from the system.
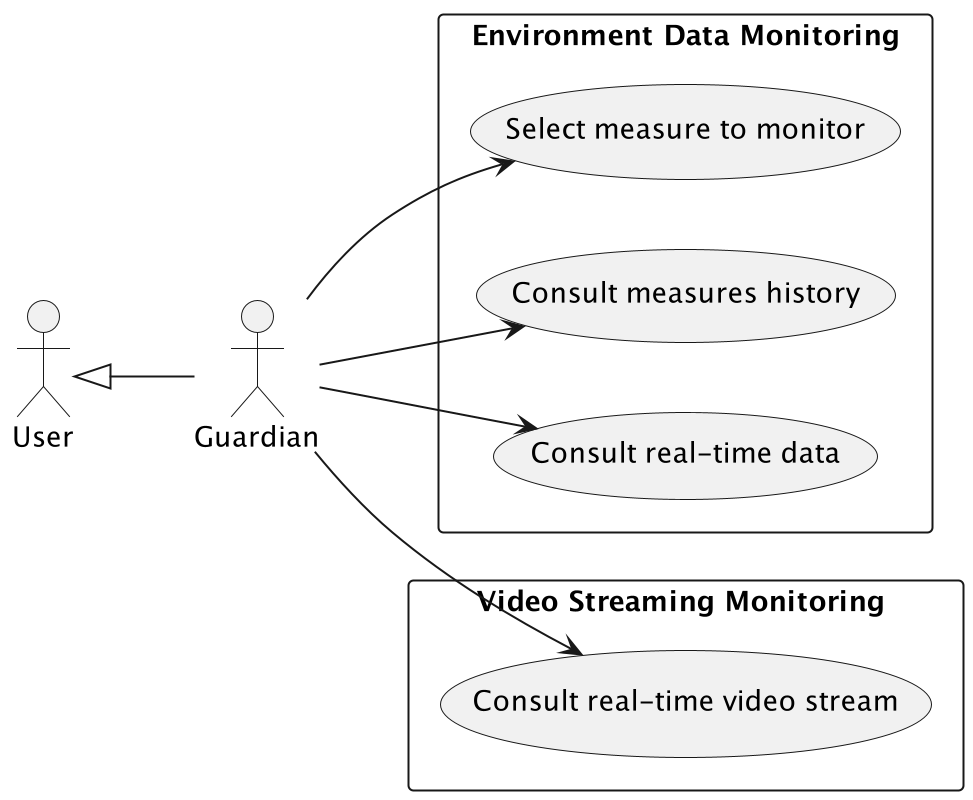
Environment Data Monitoring
A registered User can consult the environment data in real-time. The user can select a monitoring measure and consult the measure information. This is possible only if the user has access to the device depending on the location permissions.
-
Consult real-time environment data.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The device is federated in the system.
- The device exposes some capabilities; in particular, the sensing capabilities.
- The device is providing real-time data.
- The user has access to the location in which the device is located
- Post condition:
- The user can see the real-time data and choose the desired monitoring measure.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Monitoring" section and select the device to monitor.
- The user selects the monitoring measure.
- The system retrieves the real-time data and shows it to the user.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user can see the real-time data with an interval that depends on the device capabilities.
- The user can see the monitoring measure and unit in a chart.
- The user can see the last value of the monitoring measure.
- Extensions:
- The device is not providing real-time data (error message).
- The system shows only measures supported by device capabilities.
-
Consult measurements history.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The device is federated in the system.
- The device has provided some data to the system.
- Post condition:
- The user can see the measurements history.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "History."
- The user selects measurements on the drop down menu.
- The system retrieves the measurements history and shows it to the user.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user can see the measurements history.
Video Streaming Monitoring
A registered User can consult the video streaming produced by a specific camera in real-time. The user can see the video streaming only if he has access to the device depending on the permissions.
-
Consult video streaming.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The device is federated in the system.
- The device exposes some capabilities; in particular, the video streaming capability.
- The device is active and providing video streaming.
- The user has access to the location in which the device is located.
- Post condition:
- The user can see the video streaming produced by the camera.
- The produced video streaming is in real-time and available for the alarm service in case of security rules.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Video Streaming" section and selects the camera to monitor.
- The system retrieves the video streaming and shows it to the user.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user can see the video streaming produced by the camera in real-time.
Alarm Management
A registered User can consult the alarm history and create security rules. The user can define the conditions that trigger an alarm and update/delete the security rules. A component of the alarm service will check the security rules and trigger an alarm if the conditions are satisfied, notifying the user.
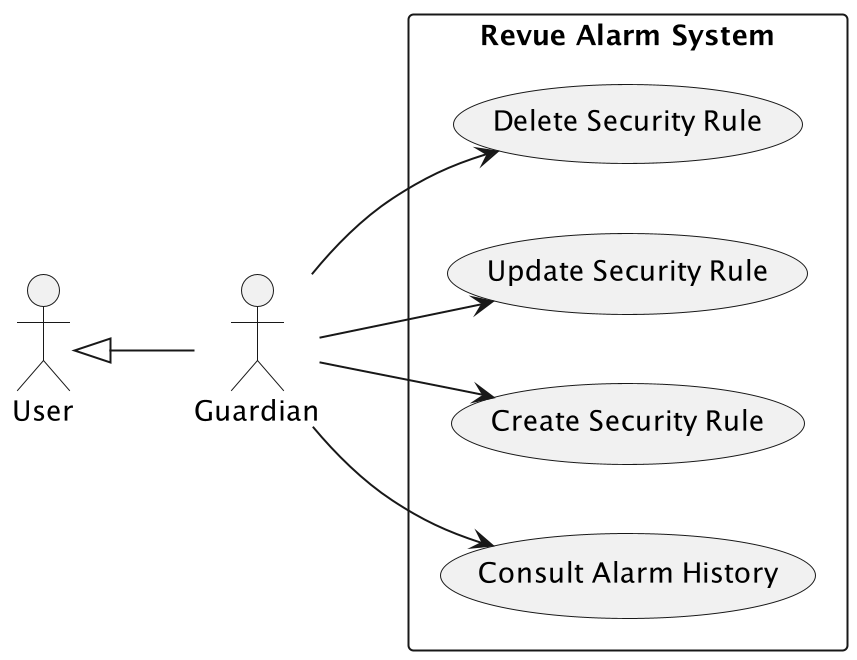
-
Consult alarm history.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The alarm service has triggered some alarms.
- Post condition:
- The user can see the alarm history.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "History" section.
- The user selects from the drop down menu the alarm property to consult: "Intrusions" or "Outliers."
- The system retrieves the alarm history and shows it to the user according to his choice.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user can see the alarm history.
- The user can see the alarm type, the device that triggered the alarm, the date and time of the alarm. Extensions:
- The alarm service has not triggered any alarm yet.
-
Create security rule.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The device is federated in the system.
- The device exposes some capabilities.
- The device is providing real-time data (streaming or environment data).
- Post condition:
- The user can see the security rule in the security rule list.
- The alarm service will check the security rule and trigger an alarm if the conditions are satisfied (also a notification will be sent).
- The user can see the alarm in the alarm history.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Security Rule" section and open the "Add Security Rule" popup.
- The user fills the security rule description.
- The user selects the device to monitor.
- The user fills the security rule settings, by either:
- Selecting the monitoring measure or the object class to monitor and recognize.
- Setting the accepted range value.
- The user selects the time interval to check the condition.
- The user selects the contacts to notify in case of alarm.
- The user selects the "Create" button.
- The system creates the security rule, and the alarm service will start checking the security rule due to his properties.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The security rule is created in the system.
- The user can see the security rule in the security rule list.
- The alarm service will check the security rule and trigger an alarm if the conditions are satisfied.
- The user can see if the rule is currently active or not.
- The user can see the contacts to notify in case of alarm.
- Extensions:
- The device is not providing real-time data, so nothing will be monitored.
-
Update security rule.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The security rule is created.
- The user can see the security rule in the security rule list.
- Post condition:
- The user can see the updated security rule in the security rule list.
- The alarm service will check the updated security rule and trigger an alarm if the conditions are satisfied (also a notification will be sent).
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Security Rule" section and selects the security rule to update.
- The user clicks on the "Update" icon.
- The user updates the security rule description, time slot or contacts to notify.
- The user clicks the "Update" button.
- The system updates the security rule and the alarm service will start checking the security rule according to its new property
- Main Success Scenario:
- The security rule is updated in the system.
- The user can see the updated security rule in the security rule list.
- The alarm service will check the updated security rule and trigger an alarm if the conditions are satisfied.
-
Delete security rule.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The security rule is created.
- The user can see the security rule in the security rule list.
- Post condition:
- The alarm service will not consider the deleted security rule anymore.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Security Rule" section and selects the security rule to delete.
- The user clicks on the "Delete" icon.
- The system deletes the security rule.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The security rule is deleted from the system.
- The user can't see the deleted security rule in the security rule list.
- The alarm service will not consider the deleted security rule anymore.
Notification Management
A registered User can consult the notification history. The user can see the notifications sent by the system. Moreover, the user can see the notification type, the date and other notification properties. When an alarm is triggered, the system will send a notification to the contacts specified in the security rule and in real-time if some users are logged in the system.
-
Consult notification history.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system.
- Post condition:
- The user can see the notification history.
- Flow:
- The user moves to the "Notification" section.
- The system retrieves the notification history.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user can see the notification history.
- The user can see the notification type, the date and other notification properties.
- Extensions:
- No notification has been sent yet.
-
Consult real-time notification.
- Actor: User
- Precondition:
- The user is logged in the system and online.
- An alarm is triggered.
- Post condition:
- The user can see the real-time notification.
- Flow:
- The user is logged in the system.
- The system sends a notification to the user.
- The user can see the notification in real-time and consult it.
- Main Success Scenario:
- The user can see the real-time notification.
- The user can see the notification type, the date and other notification properties.